russian dwarf hamster


The Russian Dwarf Hamster
The Russian dwarf hamster (Phodopus sungorus), is also called Dzungarian or Siberian dwarf hamster. This adorable little hamster is a small rodent native to Siberia and parts of Northeast China and Mongolia. This hamster species is known for its cute appearance and friendly nature. They have a stocky body with a short tail, soft fur and large eyes. Russian dwarf hamsters are popular as pets because of their small size and relatively easy care.
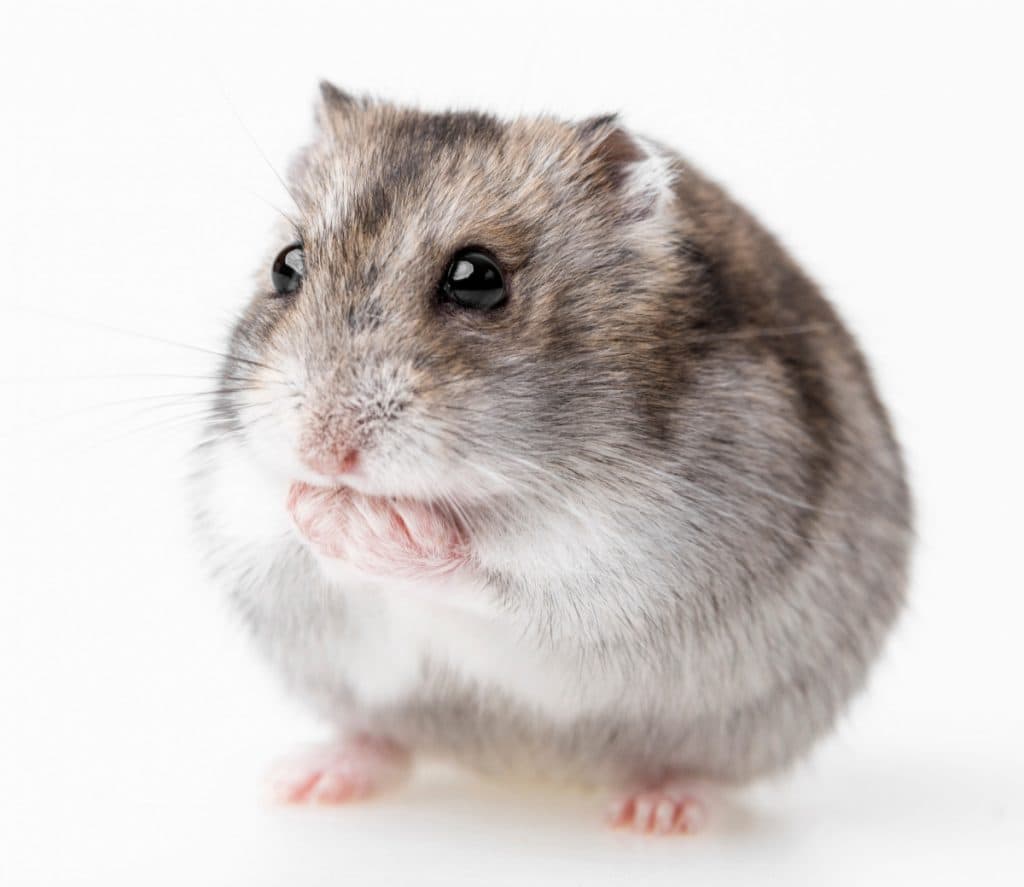


Name Dutch: russian dwarf hamster
Scientific name: Phodopus sungorus
Origin: The steppe region of northern Kazakhstan and Manchuria and southwestern and central Siberia
Age: 1,5 years
Height: 7 - 10 cm
Wearing time: 19-21 days
Birth: Livebards
Nest Size: approx. 5-6 boy
Activity: Twilight and Night Active
Legislation: not
Stay: Terrarium, Aquarium or Rodent Cage
Minimum size: 80x50cm
Food: The diet of the Russian dwarf hamster consists of the seeds of at least 51 different plant species and insects.



The appearance of the Russian dwarf hamster
The Russian dwarf hamster is exactly in between the Campelli and Roborovski dwarf hamster in size.
It is on average about 7 to 10 cm long and weighs about 50 grams on average.
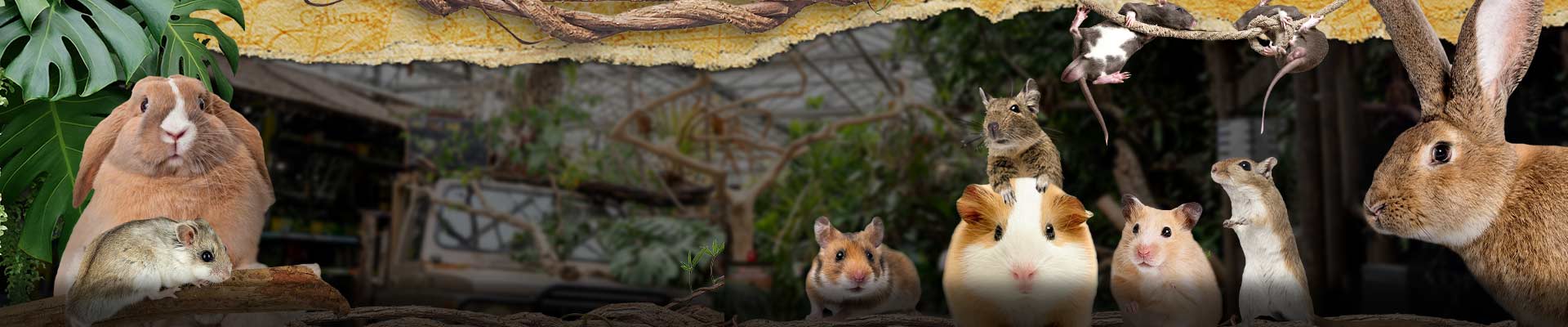
The wild color Russian dwarf hamster is dark brown with a thick dorsal stripe across its back and head, which is darker than the rest of its fur. The belly of the Russian is light brown and on both sides he has a clear three-bow line.
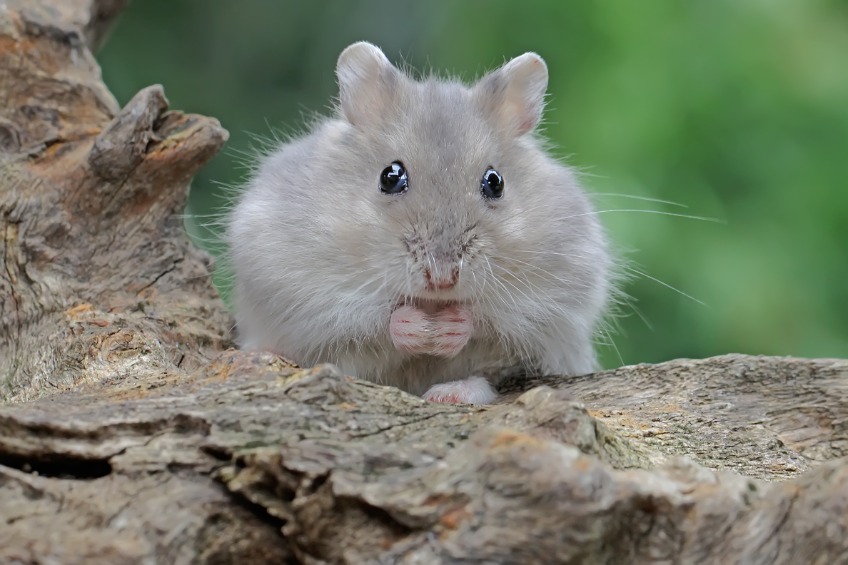
The unique thing about the Russian dwarf hamster is that these are the only hamsters that can produce a winter coat during the winter. They then become completely white. They are less noticeable in their environment, which also turns completely white in the winter months.
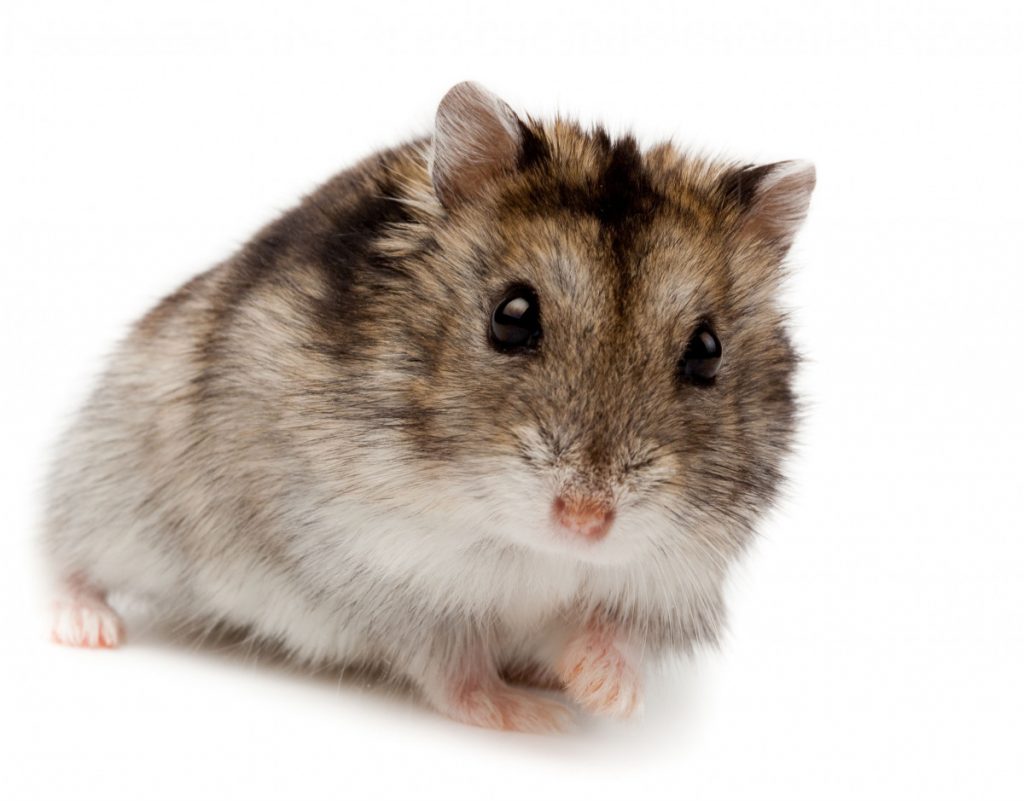

The behavior of the Russian Dwarf Hamster
The Russian dwarf hamster is easier to handle than the Roborovski dwarf hamster and tamer than the Campbelli dwarf hamster. Russians are very good, but also lazy diggers and they don't like it very much! They would much rather take an old hole than dig one themselves.
It's funny that many hamsters mainly toss around and don't necessarily dig to make a corridor. You can recognize this because they mainly throw the ground cover to the side to look under it. A hamster can toss shallowly but also deeper in the bottom. This behavior is usually seen in animals that are given food scattered around rather than in a fixed place in a food bowl.
The Russian dwarf hamster doesn't hibernate like other hamsters can, but they can enter a type of resting phase known as hibernation or torpor. The heart rate, breathing, body temperature and metabolism then drop to an absolute minimum and the hamster feels limp and cold. He eats and drinks, but a lot less.
Russians are mainly active in the evening and at night, although they also want to wake up during the day and come and have a look if they hear something. They are very active, curious and inquisitive by nature and are therefore super fun to watch!


Caresheet
The Russian hamster prefers to keep you alone. The only other option is to keep a pair, consisting of a male and a female. Keep in mind that you can expect a litter of young about every 20 days.
In the wild, Russian dwarf hamsters live in pairs of a male and a female, semi-solitary, in an area that is at least about 1000m2 in size. Within this area, the male is not monogamous, but can mate with several females. If two males meet, they will try to chase each other off because they don't tolerate competition in their area.
Females, on the other hand, have free access to the male's territory, but see each other as competitors. They pose a threat to each other's young and are therefore often even fiercer against each other than males. The fewer other females and young there are, the more food and attention MY boy and I get.
The front legs of the Russian dwarf hamster have four toes and are therefore perfect for digging, but not for climbing. Russians are therefore also very bad climbers. Besides just not being built for it, they don't see depth either. A high bar cage is therefore absolutely not suitable, they will climb out of curiosity, but will drop themselves and can end up very wrong.
To be able to dig well, they need a good layer, at least 20 cm, of ground cover. A terrarium where the doors are at the front and a bit higher is most suitable, because you can really see the corridors they dig! But an aquarium or (finely barred) cage with a deep bottom is also suitable.
We recommend 80x50cm as a minimum size for a Russian. bigger is always better of course!
Male or Female?
How can you tell if your Russian dwarf hamster is male or female? To see that, you have to turn the hamster on its back. You can recognize a female Russian dwarf hamster by this; The genital opening and the anus are very close together. This creates a small bald area.
How do you recognize a female?
The back of a female hamster is nicely round, you can see this best when you look at the hamster from above. Female Russians have clearly visible nipples that run upwards in a V-shape from the genital opening.
How do you recognize a male?
The sex organ of a male hamster is a little further away from the anus than that of the female. The hairs form a stripe between them. In adult males, the scrotum is clearly visible. Seen from above, the bottom of a male Russian dwarf hamster is more pointed.
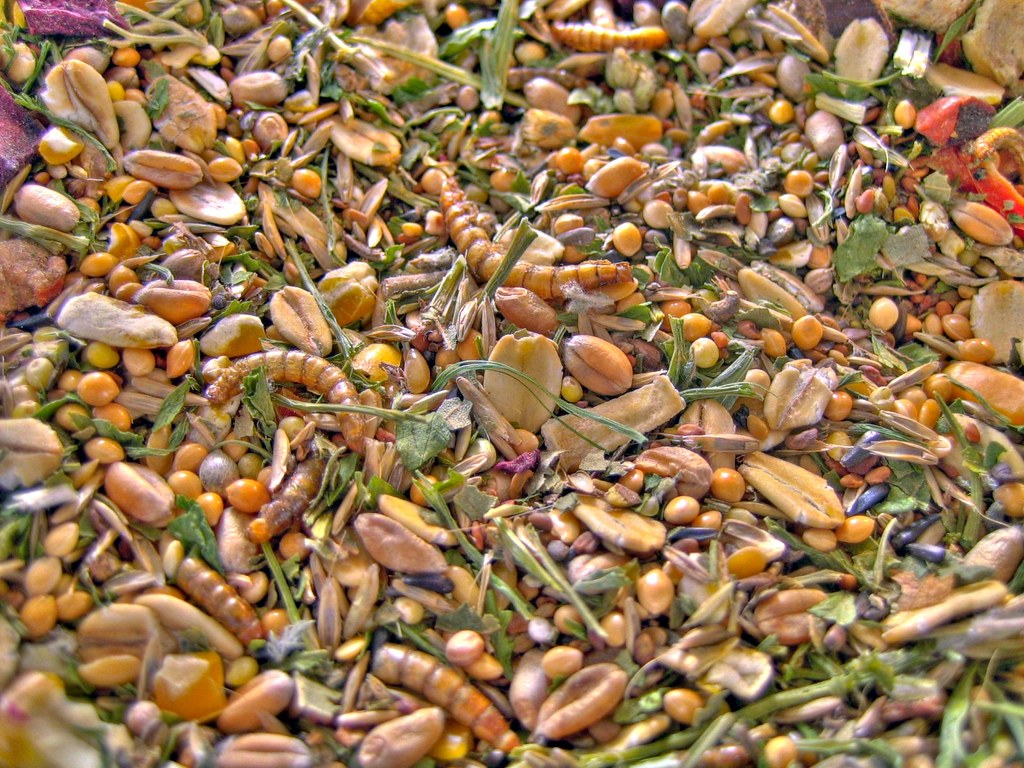



What does the Russian dwarf hamster eat?
Hamsters eat about 10% of their body weight per day, which amounts to about 5 grams per hamster.
Hamsters are mainly seed eaters (granivores). The diet of the Russian dwarf hamster consists of several 51 different plant species, of which it mainly eats the seeds.
Insects are also a major part of the Russian diet.
Hamster Pellets or Mixed Hamster Food?
There are many different hamster foods. Some consist only of pellets. This means that each kibble contains exactly the same ingredients and nutritional value. As a result, the hamster can not only extract the tasty seeds and the Russian always gets enough nutrients.
There are also foods that are composed of all different seeds and kernels, this is called mixed or mixed food. With this food, the hamster has more variety and can choose what to eat first and what to save for later. The advantage is that this is more similar to the natural diet of the Russian dwarf hamster. The risk with mixed food, however, is that the hamster will only pick out the seeds it likes best and leave the rest.
Is mixed food always bad? No definitely not! Mixed food is just as good as hamster pellets, but we should not spoil the hamster too much! If you give the Russian dwarf hamster a full bowl of food to choose from every day, he will certainly do that, but if you feed your Russian only 2 to 3 teaspoons of food per day (he doesn't need more) he will eat everything neatly.
You can also alternate it perfectly by giving your Russian dwarf hamster, for example, hamster pellets during the week and a mixed diet on the weekend or mix one day and pellets the next.


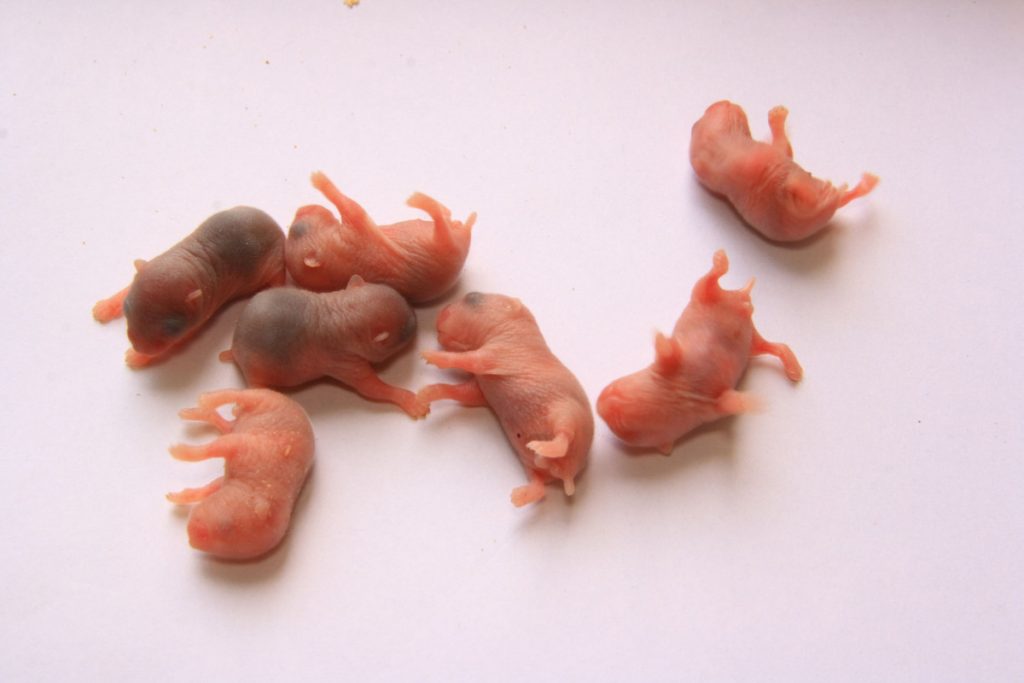
Young Russian Dwarf Hamsters
Young Russian dwarf hamsters are of course very cute, but it is not advisable to just put a male and a female together and hope that it goes well.
You need a lot of experience and knowledge of hamsters and raising young hamsters is a time-consuming job and a new home must also be found for all young Russians.
If you do want a litter from your Russian dwarf hamster, it is important to know that Russians are fertile from the age of 4 weeks. This is of course still too young to be a mother. It is best to wait until your female hamster is 3 months old, as she has only just grown at this point.
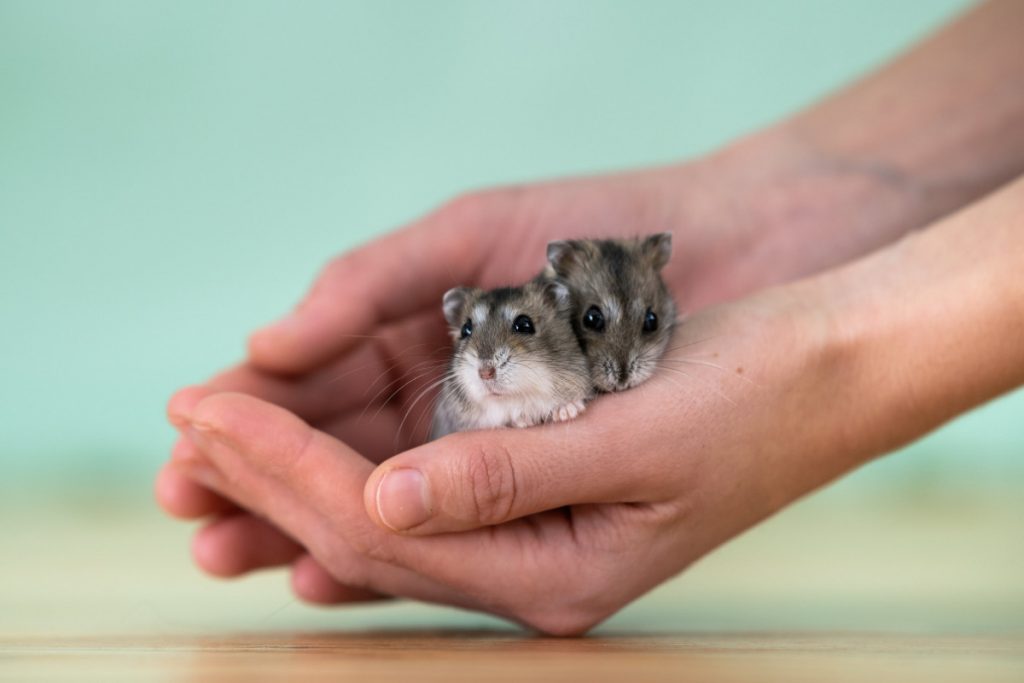


Pairing Russian Dwarf Hamsters
Then it's time to meet the father-to-be! It is best to introduce the hamsters to neutral territory. First you put the male in the mating area and before you put the female there, let him sniff her backside. This way the male knows that the hamster you add is a female.
Important! Stay with them during the introduction. you must be able to intervene if the hamsters start fighting. The coupling is successful when the hamsters have sniffed each other after a while and start doing their own thing.
the female is willing every 4 to 5 days for about 12 hours. That means she accepts the male. If the coupling does not work the first time, you can safely try again the following 5 days, until she does allow the male, the mating itself is usually at night.
The Pregnancy of a Russian Dwarf Hamster
The gestation period of the Russian dwarf hamster is about 19 to 21 days.
During pregnancy, your hamster may become more excitable and nervous. She gains about 13 grams during her pregnancy and especially in the last days before delivery and the first period after that, she needs some extra proteins. You can give these in the form of some extra mealworms or possibly a few dog chunks.
Just before your due date, make sure you've changed the enclosure and added some extra nesting material.

Hurrah! We have a litter of young Russian Dwarf Hamsters
Hamsters are mammals and give birth to their young live, just like humans. Most dwarf hamsters give birth at night or early in the morning.
After each baby she cleans up and goes to another place in the cage to bring the next baby into the world. When the last hamster is born, the mother hamster takes them all to the nest and covers them with bedding.
It is very important that you leave the nest alone! If you touch the young hamsters, they get a different smell, after which the mother hamster no longer recognizes them.
On average, a hamster has 5 to 6 young that are born naked, blind and deaf. They weigh no more than 2 grams at birth and are about a centimeter in size.
What do you need for a Russian Dwarf Hamster
How nice that you have decided that the Russian Dwarf Hamster will be your pet! What do you need? To help you on your way, we have already prepared this handy shopping list for you:
• stay (80×50)
• ground cover
• nesting material
• running wheel (ø 20cm)
• at least 1 house
• food bowl
• water bowl/bottle
• sandbox + bath sand
• gnawing material
• nutrition
• snacks















